metallic glass nanostructures fabrication properties and applications Metallic glass nanostructures: Forming strategies and functional applications Ning Li a, *,1, Jie Pan a,1, Ze Liu b, Lin Liu a a State Key Laboratory of Material Processing and Die & Mould .
Graybar has a variety of enclosures including underground, fiber optic, commercial, industrial, and residential to help with these goals. Shop our large selection of electrical enclosures to help .
0 · Metallic glass nanostructures: fabrication, properties, and
1 · Metallic glass nanostructures: fabrication, properties,
2 · Metallic glass nanostructures: Forming strategies and functional
3 · Metallic glass nanostructures: Fabrication, properties,
Our steel shelf brackets collection contains simple fixed designs for easy installation, models with integrated hooks for extending your closet possibilities, and floating shelf brackets that create a clean and spacious look in any room.
Metallic glass nanostructures: fabrication, properties, and
Here, we review the recent developments in fabrication and characterization of metallic glass (MG) nanostructures. The focus is on sub-micron structures . Abstract. Remarkable progress has been made in fabrication and characterization of metal nanostructures because of their crucial role in energy conversion, nanophotonics, . Here, we review the recent developments in fabrication and characterization of metallic glass (MG) nanostructures. The focus is on sub .
This review discusses the various physical mechanisms underlying different nanofabrication techniques of MGs. The article opens with versatile forming strategies .
Metallic glass nanostructures: fabrication, properties,
Metallic glass nanostructures: Forming strategies and functional
Here, we review the recent developments in fabrication and characterization of metallic glass (MG) nanostructures. The focus is on sub-micron structures synthesized by unconventional thermoplastic techniques.Metallic glass nanostructures: Forming strategies and functional applications Ning Li a, *,1, Jie Pan a,1, Ze Liu b, Lin Liu a a State Key Laboratory of Material Processing and Die & Mould .allows chemistry optimization for technological usage of metallic glass nanostructures, and also enables the fundamental study on size, composition and fabrication dependences of metallic glass .
Antibacterial activity, cytocompatibility, and thermomechanical stability of Ti40Zr10Cu36Pd14 bulk metallic glass Amir Rezvan, Elham Sharifikolouei, Alice Lassnig, Viktor Soprunyuk, Christoph Gammer, Florian Spieckermann, Wilfried Schranz, Ziba Najmi, Andrea Cochis, Alessandro Calogero Scalia, Lia Rimondini, Marcello Manfredi, Jürgen Eckert, Baran Sarac
Abstract: This brief review reports the recent advancement of metallic glasses and metallic glass nanostructures for functional electrocatalytic applications.Metallic glasses (MGs) or amorphous metals result from quenching the melts at a high cooling rate (e.g., 10 6 K/s), bypassing crystallization.Metallic glasses are devoid of long-range translational order, no .scientific article published on 03 January 2014. Metallic glass nanostructures: fabrication, properties, and applications Q38175322)Fabrication of metallic glass nanoporous membranes, however, is difficult with existing methods. . The metallic glass nanostructures were grown using multi-COAD illustrated in Fig . concept, properties and device applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 1247–1258 (2011). [Google Scholar] Kim D., Giermann A. L. & Thompson C. V. Solid-state .
In addition to extensive efforts in the fabrication of nanostructures, current research and development of nanostructures also focus on the investigation of fundamental material properties, including mechanical, electrical, and optical properties at the nanoscale, and the development of novel applications in a broad range of engineering fields.Abstract: This brief review reports the recent advancement of metallic glasses and metallic glass nanostructures for functional electrocatalytic applications. Metallic glasses (MGs) or amorphous metals result from quenching the melts at a high cooling rate (e.g., 10 6 K/s), bypassing crystallization.Metallic glasses are devoid of long-range translational order, no defects like .
https schneider-electric.box.com s 5w8hken8chvd81ofu9q3sxjjapqrnd2t
Chirality, the property that an object cannot coincide with its mirror image arising from lack of mirror symmetry, is ubiquitous in nature at various length scales. The physical and chemical properties are strongly related to the nature of chiral complexes, playing a significant role in various fields such as photonics, biochemistry, medicine and catalysis. In particular, the recent .
chemical and optical properties, which are largely believed to be the result of surface and quantum confinement effects[4, 5]. Remarkably, this trend has found traction in the metallic glass field where metallic glasses nanostructures (MGNs) demonstrate an important role in many applications such as In this study we report periodic and crumpled metallic glass nanostructures that can accommodate a large amount of stretching. . Fabrication, properties, and applications. Article. Full-text .Traditional applications are mainly based on the bulk metallic properties. New applications exploit the novel properties of metal . Recent research has likewise been devoted to the fabrication of porous Au nanostructures such as porous Au nanoparticles or nanowires . when mechanical stress is applied to the silica glass 22, 23. . Metals of hybrid nano-/microstructures are of broad technological and fundamental interests. Manipulation of shape and composition on the nanoscale, however, is challenging, especially for .
Recent advances in metallic glass nanostructures (MGNs) are reported, covering a wide array of synthesis strategies, computational discovery, and design solutions that provide insight into . This website requires cookies, and the limited processing of your personal data in order to function. By using the site you are agreeing to this as outlined in our privacy notice and cookie policy.
This review summarizes this specific research field, introduces the properties and applications of metallic glass, the processing characteristics of femtosecond lasers and nanosecond lasers, and explains the complex process between laser and metallic glass from a microscopic perspective. Multicomponent metallic glass films inheriting the superior mechanical properties and wide supercooled liquid regions of their bulk counterparts attract increasing attentions for applications in . A comprehensive discussion of commonly employed kinetic parameters and their connection with the unique material structures of MGNs on individual electrocatalytic reactions is made, including the hydrogen evolution reaction, oxygen reduction reaction, and alcohol (methanol or ethanol) oxidation reaction. Recent advances in metallic glass nanostructures .
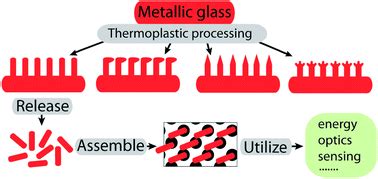
An amorphous–nanocrystalline alloy is generally a dual-phase material made up of a metallic amorphous phase and nano-sized crystals. On the one hand, amorphous metals, which lack long-range translational symmetry and crystalline defects, possess large elastic strain limit, superb strength, excellent thermo-plastic formability, and good corrosion/wear resistance [[1], .
Remarkable progress has been made in fabrication and characterization of metal nanostructures because of their crucial role in energy conversion, nanophotonics, nanoelectronics, and biodiagnostics. Less emphasis has been placed on the synthesis of nanostructures from metallic alloys, which are better suited
In general, the Raman shift is expressed in units of cm −1, and the corresponding spectrum is called the Raman spectrum.Despite the potential in molecular sensing and obtaining molecular structural information with the high spatial resolution achieved through diffraction limited wavelength, the practical applications of this technique are largely limited even now by the . Nanotechnology has brought forward the design of various gold nanostructures with a vast variety of different nanoarchitectures. The outstanding optical properties of gold nanoparticles and flower or waxberry-like gold nanostructures – a result of surface-plasmon oscillations – have made these nanomaterials very attractive for applications in sensing, .
Metallic glass nanostructures: fabrication, properties, and applications. Nanoscale, 6 (2014), pp. 2027-2036. Crossref View in Scopus Google Scholar [23] . High-power fiber laser welding and its application to metallic glass Zr 55 Al 10 Ni 5 Cu 30. Mater. Sci. Eng. B., 148 (2008), pp. 105-109. View PDF View article View in Scopus Google . Thin film metallic glasses: properties, applications and future. J. Appl. Phys., 127 (2020), p. 16. Google Scholar . Few-layer thin-film metallic glass-enhanced optical properties of ZnO nanostructures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 9 (2017) . Fabrication of ordered metallic glass nanotube arrays for label-free biosensing with diffractive . On the one hand, the derived amorphousenanocrystalline alloys may inherit the unique properties from either the amorphous or the nanocrystalline "template", such as outstanding magnetic properties .To specifically spotlight the Nanoscale Accepted Manuscript fundamentally critical to most practical applications; therefore, how metal atoms form Page 3 of 34 Nanoscale newly emerged material, this review paper investigates the fabrication and application of helical metallic structures with micro- and nano-scale dimensions.
Metallic glass nanostructures: Fabrication, properties,
Crafted of wood in a gloss white finish, this jewelry box strikes a rectangular silhouette measuring 5.5" H x 14" W x 8" D overall. Satin metal hardware lends contemporary appeal to the outer box, while soft leaf-green faux-suede lining protects jewelry from scratches and abrasions within.
metallic glass nanostructures fabrication properties and applications|Metallic glass nanostructures: Fabrication, properties,