box plot equal variance normal distribution Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left, or skewed to the right, and estimate the . Choose from our selection of underground junction boxes, including corrosion-resistant washdown enclosures, indoor enclosures, and more. In stock and ready to ship.
0 · how to calculate box distribution
1 · equal variance in box plot
2 · deduce variance box plot
3 · boxplot to deduce variance
4 · box plot variation
5 · box plot variance
6 · box plot and median distribution
7 · box distribution chart pdf
By understanding the function of junction boxes, using the right tools and materials, following a step-by-step guide, and avoiding common mistakes, DIY enthusiasts can tackle wiring projects with confidence.
how to calculate box distribution
I'm trying to decide if the variance in these groups in this boxplot are equal, so how can I tell how much variation each group has just looking at the box plot? And how can I tell if they all have equal variance? Here is the boxplot:For example, a parametric $t$-test assumes normal distributions with equal variance .
For example, a parametric $t$-test assumes normal distributions with equal variance (though it's fairly robust to violations of the latter given equal sample sizes), so I wouldn't recommend that test for comparing my population .
metal fabrication central nj
Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left, or skewed to the right, and estimate the . The most common way to measure variation in a box plot is by analyzing the interquartile range. The interquartile range represents the spread of the middle 50% of the data. In a box plot, it is represented by the width of the . Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum .What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot .
The common data assumptions are: random samples, independence, normality, equal variance, stability, and that your measurement system is accurate and precise. I addressed random samples and statistical . Using box plots we can better understand our data by understanding its distribution, outliers, mean, median and variance. Box plot packs all of this information about our data in a single.
If I plot some data in function of a categorical variable in R, I get the standard boxplot. However, the boxplot displays non-parametric statistics (quantiles) that don't seem appropriate for . I'm trying to decide if the variance in these groups in this boxplot are equal, so how can I tell how much variation each group has just looking at the box plot? And how can I tell if they all have equal variance? Here is the boxplot:
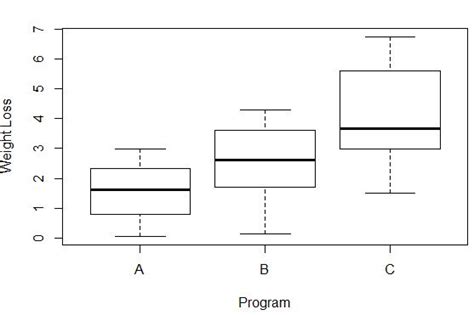
For example, a parametric $t$-test assumes normal distributions with equal variance (though it's fairly robust to violations of the latter given equal sample sizes), so I wouldn't recommend that test for comparing my population 2 to population 1 (the normal distribution). Boxplots offer a visual way to check the assumption of equal variances. The variance of weight loss in each group can be seen by the length of each box plot. The longer the box, the higher the variance. For example, we can see that the variance is a bit higher for participants in program C compared to both program A and program B. 2.Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left, or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median. The most common way to measure variation in a box plot is by analyzing the interquartile range. The interquartile range represents the spread of the middle 50% of the data. In a box plot, it is represented by the width of the box, which ranges from the first quartile (Q1) to the third quartile (Q3)
Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot displays a ton of information in a simplified format.
The common data assumptions are: random samples, independence, normality, equal variance, stability, and that your measurement system is accurate and precise. I addressed random samples and statistical independence last time.
Using box plots we can better understand our data by understanding its distribution, outliers, mean, median and variance. Box plot packs all of this information about our data in a single.
If I plot some data in function of a categorical variable in R, I get the standard boxplot. However, the boxplot displays non-parametric statistics (quantiles) that don't seem appropriate for normally distributed data. I'm trying to decide if the variance in these groups in this boxplot are equal, so how can I tell how much variation each group has just looking at the box plot? And how can I tell if they all have equal variance? Here is the boxplot: For example, a parametric $t$-test assumes normal distributions with equal variance (though it's fairly robust to violations of the latter given equal sample sizes), so I wouldn't recommend that test for comparing my population 2 to population 1 (the normal distribution). Boxplots offer a visual way to check the assumption of equal variances. The variance of weight loss in each group can be seen by the length of each box plot. The longer the box, the higher the variance. For example, we can see that the variance is a bit higher for participants in program C compared to both program A and program B. 2.

Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left, or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median. The most common way to measure variation in a box plot is by analyzing the interquartile range. The interquartile range represents the spread of the middle 50% of the data. In a box plot, it is represented by the width of the box, which ranges from the first quartile (Q1) to the third quartile (Q3) Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.
What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot displays a ton of information in a simplified format. The common data assumptions are: random samples, independence, normality, equal variance, stability, and that your measurement system is accurate and precise. I addressed random samples and statistical independence last time.
Using box plots we can better understand our data by understanding its distribution, outliers, mean, median and variance. Box plot packs all of this information about our data in a single.
metal fabrication colorado springs
IP68 Waterproof Junction Box Outdoor, 3 Way Underground Electrical Junction Box, Plastic Electrical Box with Terminal Block, Suitable for LED Landscape Lighting, Garden Lights, Solar Power and More
box plot equal variance normal distribution|equal variance in box plot