box plot based on frequency distribution When estimating the median and quartiles of a set of data from a cumulative frequency graph, it is very easy to then draw a box plot of this data. Step-by-step guide: Cumulative frequency (Example 4) (coming soon) What is a box plot? . Wayne Roofing and Sheet Metal is a family-operated business in Goldsboro, North Carolina, boasting a cherished history since 1947. What makes us unique? Not only do we excel in installing high-grade metal and shingle roofs, but we also boast the distinctive capability to produce our own custom metal suited precisely for your roofing needs.
0 · math net box plot
1 · how to print frequency boxplot
2 · example of a box plot
3 · box plots math
4 · box plots explained
5 · box plot frequency
6 · box plot formula
7 · box plot calculation
$9.60
You'd like a box plot of the frequency of the "cut" column.but that column is qualitative. Boxplots typically visualize the five-number summary of a quantitative data. (ie, the quartiles and outliers). To show the frequency of the different .A box plot, also referred to as a box and whisker plot, displays how elements in a data set are distributed throughout the set using a five number summary: Minimum - smallest value in the .
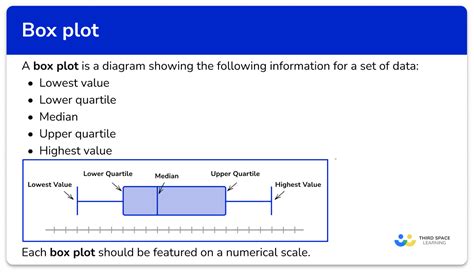
A box plot is a diagram which provides a quick visual summary of the distribution of a data set. It makes drawing conclusions easier and is useful for comparing two sets of data. When data is.
When estimating the median and quartiles of a set of data from a cumulative frequency graph, it is very easy to then draw a box plot of this data. Step-by-step guide: Cumulative frequency (Example 4) (coming soon) What is a box plot? . Box plots are good at portraying extreme values and are especially good at showing differences between distributions. However, many of the details of a distribution are not revealed in a box plot, and to examine these details . A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a graphical representation of the distribution of a dataset. It summarizes key statistics such as the median, quartiles, and outliers, providing insights into the spread and .
Box plots are often used for comparing two sets of data. Both box plots will be drawn one above the other on the same scale on the x-axis; They are useful for comparing data because it is easy to see the main shape of the .
Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum .
This article describes 4 easy ways to plot frequency distribution in Excel. Download & exercise the workbook to learn the methods easily.What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot displays a ton of information in a simplified format.
You'd like a box plot of the frequency of the "cut" column.but that column is qualitative. Boxplots typically visualize the five-number summary of a quantitative data. (ie, the quartiles and outliers). To show the frequency of the different cuts, I think a bar plot might be more appropriate?A box plot, also referred to as a box and whisker plot, displays how elements in a data set are distributed throughout the set using a five number summary: Minimum - smallest value in the set; it is the left-most point of the plot. First/lower quartile (Q1) - the number below which 25% of the data in the set lies.A box plot is a diagram which provides a quick visual summary of the distribution of a data set. It makes drawing conclusions easier and is useful for comparing two sets of data. When data is.When estimating the median and quartiles of a set of data from a cumulative frequency graph, it is very easy to then draw a box plot of this data. Step-by-step guide: Cumulative frequency (Example 4) (coming soon) What is a box plot? In order to .
math net box plot
Box plots are good at portraying extreme values and are especially good at showing differences between distributions. However, many of the details of a distribution are not revealed in a box plot, and to examine these details one should create a histogram and/or a stem and leaf display.
how to print frequency boxplot
A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a graphical representation of the distribution of a dataset. It summarizes key statistics such as the median, quartiles, and outliers, providing insights into the spread and central tendency of the data. Box plots are often used for comparing two sets of data. Both box plots will be drawn one above the other on the same scale on the x-axis; They are useful for comparing data because it is easy to see the main shape of the distribution of the data from a box plot; The key features of a box plot Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.A boxplot generally plots a distribution rather than a summary of data. Instead, try something like boxplot(var1, subset=cut(var2, 12)). That way, the function is doing the summarization work for you. Take a read of ?boxplot.
What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot displays a ton of information in a simplified format.
You'd like a box plot of the frequency of the "cut" column.but that column is qualitative. Boxplots typically visualize the five-number summary of a quantitative data. (ie, the quartiles and outliers). To show the frequency of the different cuts, I think a bar plot might be more appropriate?A box plot, also referred to as a box and whisker plot, displays how elements in a data set are distributed throughout the set using a five number summary: Minimum - smallest value in the set; it is the left-most point of the plot. First/lower quartile (Q1) - the number below which 25% of the data in the set lies.
A box plot is a diagram which provides a quick visual summary of the distribution of a data set. It makes drawing conclusions easier and is useful for comparing two sets of data. When data is.
When estimating the median and quartiles of a set of data from a cumulative frequency graph, it is very easy to then draw a box plot of this data. Step-by-step guide: Cumulative frequency (Example 4) (coming soon) What is a box plot? In order to . Box plots are good at portraying extreme values and are especially good at showing differences between distributions. However, many of the details of a distribution are not revealed in a box plot, and to examine these details one should create a histogram and/or a stem and leaf display. A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a graphical representation of the distribution of a dataset. It summarizes key statistics such as the median, quartiles, and outliers, providing insights into the spread and central tendency of the data.
Box plots are often used for comparing two sets of data. Both box plots will be drawn one above the other on the same scale on the x-axis; They are useful for comparing data because it is easy to see the main shape of the distribution of the data from a box plot; The key features of a box plot Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.
the electric music box
the best stainless steel lunch box
example of a box plot
$8.38
box plot based on frequency distribution|box plot formula