electrical box conductor volume Part (B), “Box Fill Calculations,” describes the method for determining how much volume (fill) may be occupied by conductors, clamps, support fittings, devices (switches or receptacles) or equipment, and equipment grounding conductors. The answer is that the Red Wire is the Hot Wire from the switch itself. You are wiring your fixture into a junction box where buku wires come together. Hook the white to white, ground to ground and RED to the BLACK Light Fixture Wires.
0 · volume of electrical boxes
1 · standard electrical box volume
2 · how many conductors in electrical box
3 · electrical box volume chart
4 · electrical box volume calculations
5 · electrical box volume and fill calculator
6 · electrical box volume and fill
7 · box wire volume chart
SolidWorks' sheet metal tool makes designing metal parts simpler. Follow along with our SolidWorks Sheet Metal tutorial!
Part (B), “Box Fill Calculations,” describes the method for determining how much volume (fill) may be occupied by conductors, clamps, support fittings, devices (switches or receptacles) or equipment, and equipment grounding conductors. Use this box fill calculator to find the correct size of electrical utility box to fit the conducting wires, grounding wires, and devices or equipment you would need to install and have it pass the National Electrical Code®.
Enter the required parameters to precisely calculate “Box Fill" requirements for an electrical wiring box. This box fill calculator precisely estimates the total box fill volumes for electrical utility .Electrical Box Fill Table Information. Box Fill Guidelines: No matter how many ground wires, they only count as one conductor in the box. A wire running through the box counts as one wire. Each wire coming into a splice connector is .
A Volume Allowance for each conductor is counted based on the following: One for each conductor (phase conductor or grounded conductor) that terminates or splices within the box. One for the largest equipment grounding .The box fill calculators help you calculate the suitable box volume with the required capacity to fit the ground wires, conducting wires, clamps, and support fittings. Enter the number of AWG conductors. Every outlet box has a specific amount of space for conductors, devices, and fittings. We call that the box volume. You calculate box volume per 314.16(A) and box fill per 314.16(B), but make sure your 314.16(A) box volume .Box & conduit Fill Calculations What size IMC is required for 6 - 12 AWG RHH Cu conductors without outer covering and 4 -14 AWG RHH Cu Conductors with outer covering ? Table 5 – .
Our Box Fill Calculator is designed to help you determine the maximum number of conductors and devices that can be safely accommodated in an electrical box. Accurate box fill calculations .
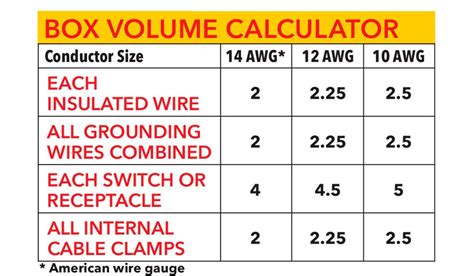
Items Contained within Box # of Conductors (not including grounds) Size (AWG) Volume Allowance Multiplier. Unit Volume (in 2) Based on Table 314.16(B) Top Box Fill (in 2) A. .
Part (B), “Box Fill Calculations,” describes the method for determining how much volume (fill) may be occupied by conductors, clamps, support fittings, devices (switches or receptacles) or equipment, and equipment grounding conductors. Use this box fill calculator to find the correct size of electrical utility box to fit the conducting wires, grounding wires, and devices or equipment you would need to install and have it pass the National Electrical Code®.Enter the required parameters to precisely calculate “Box Fill" requirements for an electrical wiring box. This box fill calculator precisely estimates the total box fill volumes for electrical utility boxes, prioritizing safety and electrical system reliability in various installations.Electrical Box Fill Table Information. Box Fill Guidelines: No matter how many ground wires, they only count as one conductor in the box. A wire running through the box counts as one wire. Each wire coming into a splice connector is counted as one wire. Each wire connecting to a device counts as one wire of that size.
A Volume Allowance for each conductor is counted based on the following: One for each conductor (phase conductor or grounded conductor) that terminates or splices within the box. One for the largest equipment grounding conductor.The box fill calculators help you calculate the suitable box volume with the required capacity to fit the ground wires, conducting wires, clamps, and support fittings. Enter the number of AWG conductors. Every outlet box has a specific amount of space for conductors, devices, and fittings. We call that the box volume. You calculate box volume per 314.16(A) and box fill per 314.16(B), but make sure your 314.16(A) box volume is .Box & conduit Fill Calculations What size IMC is required for 6 - 12 AWG RHH Cu conductors without outer covering and 4 -14 AWG RHH Cu Conductors with outer covering ? Table 5 – Cross-Sectional Area of Individual Conductors 14 AWG RHH Cu With Outer Covering = .0293 X 4 = .1172 12 AWG RHH Cu Without Outer Covering = .0260 X 6 = .1560
Our Box Fill Calculator is designed to help you determine the maximum number of conductors and devices that can be safely accommodated in an electrical box. Accurate box fill calculations are essential for ensuring compliance with electrical codes and .Items Contained within Box # of Conductors (not including grounds) Size (AWG) Volume Allowance Multiplier. Unit Volume (in 2) Based on Table 314.16(B) Top Box Fill (in 2) A. Conductor Size #1. . Copperweld CCA Conductors Now Featured in MasterSpec. A Game-Changer for Sustainable Building Design. September 24, 2024.Part (B), “Box Fill Calculations,” describes the method for determining how much volume (fill) may be occupied by conductors, clamps, support fittings, devices (switches or receptacles) or equipment, and equipment grounding conductors.

Use this box fill calculator to find the correct size of electrical utility box to fit the conducting wires, grounding wires, and devices or equipment you would need to install and have it pass the National Electrical Code®.Enter the required parameters to precisely calculate “Box Fill" requirements for an electrical wiring box. This box fill calculator precisely estimates the total box fill volumes for electrical utility boxes, prioritizing safety and electrical system reliability in various installations.Electrical Box Fill Table Information. Box Fill Guidelines: No matter how many ground wires, they only count as one conductor in the box. A wire running through the box counts as one wire. Each wire coming into a splice connector is counted as one wire. Each wire connecting to a device counts as one wire of that size.
A Volume Allowance for each conductor is counted based on the following: One for each conductor (phase conductor or grounded conductor) that terminates or splices within the box. One for the largest equipment grounding conductor.The box fill calculators help you calculate the suitable box volume with the required capacity to fit the ground wires, conducting wires, clamps, and support fittings. Enter the number of AWG conductors.
volume of electrical boxes
standard electrical box volume
Every outlet box has a specific amount of space for conductors, devices, and fittings. We call that the box volume. You calculate box volume per 314.16(A) and box fill per 314.16(B), but make sure your 314.16(A) box volume is .
Box & conduit Fill Calculations What size IMC is required for 6 - 12 AWG RHH Cu conductors without outer covering and 4 -14 AWG RHH Cu Conductors with outer covering ? Table 5 – Cross-Sectional Area of Individual Conductors 14 AWG RHH Cu With Outer Covering = .0293 X 4 = .1172 12 AWG RHH Cu Without Outer Covering = .0260 X 6 = .1560Our Box Fill Calculator is designed to help you determine the maximum number of conductors and devices that can be safely accommodated in an electrical box. Accurate box fill calculations are essential for ensuring compliance with electrical codes and .
how many conductors in electrical box
electrical box volume chart
electrical box volume calculations

Fab shops typically employ several welding methods, including spot welding, tack welding, fuse welding, stitch welding, plug welding, seam/fillet welding, MIG welding, and TIG welding, each with unique applications and characteristics.
electrical box conductor volume|electrical box volume chart