electric field metal box ContinuousA continuous Faraday shield is a hollow conductor. Externally or internally applied electromagnetic . See more Welded Sheet Metal Manufacturing, LLC located at 745 Greenway Dr, Pittsburgh, PA 15204 - reviews, ratings, hours, phone number, directions, and more.
0 · magnetics
1 · What is a Faraday cage?
2 · Shielding from electric/magnetic field using a metal box
3 · Introduction to Practical Electromagnetic Shielding
4 · How much shielding does an ungrounded metal box provide?
5 · How Faraday Cages Work
6 · Faraday cage
7 · Faraday Cage: What Is It? How Does It Work?
8 · Electrostatic Shielding
9 · Electromagnetic shielding
This groundbreaking new text connects each welding technique to a useful and creative take-home project, making exercises both practical and personal. To further enhance the learning process, every welding project includes a set of prints with specifications, like those used in production fabrication shops.
magnetics
liberty sheet metals gutter replacement
What is a Faraday cage?
Animation showing how a Faraday cage (box) works. When an external electrical field (arrows) is applied, the electrons (little balls) in the metal move to the left side of the cage, giving it a negative charge, while the remaining unbalanced charge of the nuclei give the right side a positive charge. These induced . See moreA Faraday cage or Faraday shield is an enclosure used to block some electromagnetic fields. A Faraday shield may be formed by a continuous covering of conductive material, or in the case of a Faraday cage, by a . See more• Faraday cages are routinely used in analytical chemistry to reduce noise while making sensitive measurements.• Faraday cages, more specifically dual paired seam Faraday bags, are often used in digital forensics to prevent remote wiping and alteration . See more
In 1754, Jean-Antoine Nollet published an account of the cage effect in his Leçons de physique expérimentale.In 1755, Benjamin Franklin observed the effect by lowering an . See moreContinuousA continuous Faraday shield is a hollow conductor. Externally or internally applied electromagnetic . See more• Anechoic chamber• Anti-static bag• Conductive textile• Foil hat• Gauss's law• Mobile phone jammer See more

• Faraday Cage Protects from 100,000 V:: Physikshow Uni Bonn• Notes from physics lecture on Faraday cages from Michigan State University• Make in India Faraday Cage See more However, it's not possible to shield an electrostatic charge inside the box, therefore, you need to ground it. (And magnetostatic fields can only be shielded by a .
light junction box screw size
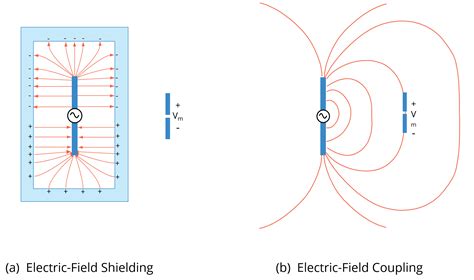
Figure 3 and Figure 4 show the general principle of a Faraday cage when an electric and magnetic field interacts with a Faraday cage. Assuming a fully enclosed metal box that serves .In electrical engineering, electromagnetic shielding is the practice of reducing or redirecting the electromagnetic field (EMF) in a space with barriers made of conductive or magnetic materials. It is typically applied to enclosures, for isolating electrical devices from their surroundings, and to cables to isolate wires from the environment through which the cable runs (see Shielded cable). Electromagne.Key concepts for practical electric field shielding are choosing a location that will intercept the stronger field lines and choosing a suitably conductive shield material. How conductive must the material be? That depends on the .This allows charges to flow (from ground) onto the conductor, producing an electric field opposite to that of the charge inside the hollow conductor. The conductor then acts like an electrostatic shield as a result of the superposition .

A metal box can shield from electric/magnetic fields by creating a barrier between the outside field and the inside of the box. The metal acts as a conductor and absorbs the . It works on the principle that when an electromagnetic field hits something that can conduct electricity, the charges remain on the exterior of the conductor rather than traveling inside. The sea-of-mobile-electrons in metal is very effective for Efield shielding; the electrons roam to where needed on the metal's surface, to oppose the incoming Efield flux .
Animation showing how a Faraday cage (box) works. When an external electrical field (arrows) is applied, the electrons (little balls) in the metal move to the left side of the cage, giving it a negative charge, while the remaining unbalanced charge of the nuclei give the right side a positive charge. These induced charges create an opposing .
The result is an opposing electric field that cancels out the field of the external object's charge inside the metal conductor. The net electric charge inside the aluminum mesh, then, is zero.
However, it's not possible to shield an electrostatic charge inside the box, therefore, you need to ground it. (And magnetostatic fields can only be shielded by a ferromagnetic box.) So, in general, a metal box will shield all EM waves and external electrostatic fields to some degree.
Figure 3 and Figure 4 show the general principle of a Faraday cage when an electric and magnetic field interacts with a Faraday cage. Assuming a fully enclosed metal box that serves as Faraday cage with the measurement cell in the inside as shown in Figure 3.
In electrical engineering, electromagnetic shielding is the practice of reducing or redirecting the electromagnetic field (EMF) in a space with barriers made of conductive or magnetic materials.Key concepts for practical electric field shielding are choosing a location that will intercept the stronger field lines and choosing a suitably conductive shield material. How conductive must the material be? That depends on the frequency or time rate-of-change of the fields.This allows charges to flow (from ground) onto the conductor, producing an electric field opposite to that of the charge inside the hollow conductor. The conductor then acts like an electrostatic shield as a result of the superposition of the two fields. A metal box can shield from electric/magnetic fields by creating a barrier between the outside field and the inside of the box. The metal acts as a conductor and absorbs the electric/magnetic energy, preventing it from entering the box.
It works on the principle that when an electromagnetic field hits something that can conduct electricity, the charges remain on the exterior of the conductor rather than traveling inside.
The sea-of-mobile-electrons in metal is very effective for Efield shielding; the electrons roam to where needed on the metal's surface, to oppose the incoming Efield flux lines, coercing that flux to only impinge on the shield metal at exactly 90 degrees.Animation showing how a Faraday cage (box) works. When an external electrical field (arrows) is applied, the electrons (little balls) in the metal move to the left side of the cage, giving it a negative charge, while the remaining unbalanced charge of the nuclei give the right side a positive charge. These induced charges create an opposing . The result is an opposing electric field that cancels out the field of the external object's charge inside the metal conductor. The net electric charge inside the aluminum mesh, then, is zero.
However, it's not possible to shield an electrostatic charge inside the box, therefore, you need to ground it. (And magnetostatic fields can only be shielded by a ferromagnetic box.) So, in general, a metal box will shield all EM waves and external electrostatic fields to some degree.Figure 3 and Figure 4 show the general principle of a Faraday cage when an electric and magnetic field interacts with a Faraday cage. Assuming a fully enclosed metal box that serves as Faraday cage with the measurement cell in the inside as shown in Figure 3.
In electrical engineering, electromagnetic shielding is the practice of reducing or redirecting the electromagnetic field (EMF) in a space with barriers made of conductive or magnetic materials.
Key concepts for practical electric field shielding are choosing a location that will intercept the stronger field lines and choosing a suitably conductive shield material. How conductive must the material be? That depends on the frequency or time rate-of-change of the fields.
This allows charges to flow (from ground) onto the conductor, producing an electric field opposite to that of the charge inside the hollow conductor. The conductor then acts like an electrostatic shield as a result of the superposition of the two fields.
A metal box can shield from electric/magnetic fields by creating a barrier between the outside field and the inside of the box. The metal acts as a conductor and absorbs the electric/magnetic energy, preventing it from entering the box. It works on the principle that when an electromagnetic field hits something that can conduct electricity, the charges remain on the exterior of the conductor rather than traveling inside.
Welding and Metal Fabrication Book pdf by Larry Jeffus. Welding and Metal Fabrication is designed to help you develop all of the skills to become a highly-paid paid versatile welder.
electric field metal box|magnetics