box that illustrates the normal distribution For a perfectly normal distribution, the mean, median, and mode will be the same value, visually represented by the peak of the curve. The normal distribution is often called the .
Our vertical mills provide high performance machining for a magnitude of applications. No matter your part, industry, or needs, there’s a Haas vertical machine perfect for your shop. Designed and manufactured in California by Haas, these spindles are custom-engineered for power, precision, and durability. Optimize your cutting conditions.
0 · normal distributions worksheet
1 · normal distributions in math
2 · normal distribution statistics pdf
3 · normal distribution lesson
4 · normal distribution graph
5 · how to find the normal distribution
6 · family of normal distributions
7 · examples of normal distribution
Hold down brackets for wood, faux wood, and Venetian blinds.
In this lesson, we'll investigate one of the most prevalent probability distributions in the natural world, namely the normal distribution. Just as we have for other probability distributions, we'll explore the normal distribution's properties, as well as learn how to calculate normal probabilities.The normal distribution is the only distribution whose cumulants beyond the first two (i.e., other than the mean and variance) are zero. It is also the continuous distribution with the maximum entropy for a specified mean and variance. Geary has shown, assuming that the mean and variance are finite, that the normal distribution is the only distribution where the mean and variance calculated from a set of independent draws are independent of each other.
Instructions: This Normal Probability grapher draw a graph of the normal distribution. Please type the population mean \mu μ and population standard deviation \sigma σ, and provide details . There are key features of the normal distribution that make it easy to visually distinguish from other graphs: the peak, asymptotic nature, and symmetry of the graph. The .TWO NEW 12 INCH TALL GALTON BOARDS WITH PASCAL'S TRIANGLE ARE AVAILABLE! They are probability demonstrators that illustrate randomness, the normal distribution, the . For a perfectly normal distribution, the mean, median, and mode will be the same value, visually represented by the peak of the curve. The normal distribution is often called the .
In a normal distribution, data is symmetrically distributed with no skew. When plotted on a graph, the data follows a bell shape, with most values clustering around a central .
Why we love it: This resource walks through multi-step examples and illustrates how the normal distribution can help us estimate the probability of an event.The normal distribution, also called the Gaussian distribution, is a probability distribution commonly used to model phenomena such as physical characteristics (e.g. height, weight, .
In this lesson, we'll investigate one of the most prevalent probability distributions in the natural world, namely the normal distribution. Just as we have for other probability distributions, we'll explore the normal distribution's properties, as well as learn how to calculate normal probabilities.
The normal distribution is a subclass of the elliptical distributions. The normal distribution is symmetric about its mean, and is non-zero over the entire real line.
Instructions: This Normal Probability grapher draw a graph of the normal distribution. Please type the population mean \mu μ and population standard deviation \sigma σ, and provide details about the event you want to graph (for the standard normal distribution , the mean is \mu = 0 μ = 0 and the standard deviation is \sigma = 1 σ = 1): There are key features of the normal distribution that make it easy to visually distinguish from other graphs: the peak, asymptotic nature, and symmetry of the graph. The normal curve is essentially a frequency polygon which is tallest (peaks) at the center and gets progressively shorter as you move further into the tails.
Normal distribution. by Marco Taboga, PhD. The normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that plays a central role in probability theory and statistics.TWO NEW 12 INCH TALL GALTON BOARDS WITH PASCAL'S TRIANGLE ARE AVAILABLE! They are probability demonstrators that illustrate randomness, the normal distribution, the binomial distribution, the central limit theorem, regression to the mean and single outcomes with one larger golden bead.
For a perfectly normal distribution, the mean, median, and mode will be the same value, visually represented by the peak of the curve. The normal distribution is often called the bell curve because the graph of its probability density looks like a bell. In a normal distribution, data is symmetrically distributed with no skew. When plotted on a graph, the data follows a bell shape, with most values clustering around a central region and tapering off as they go further away from the center. Normal distributions are also called Gaussian distributions or bell curves because of their shape.
Why we love it: This resource walks through multi-step examples and illustrates how the normal distribution can help us estimate the probability of an event.The normal distribution, also called the Gaussian distribution, is a probability distribution commonly used to model phenomena such as physical characteristics (e.g. height, weight, etc.) and test scores.In this lesson, we'll investigate one of the most prevalent probability distributions in the natural world, namely the normal distribution. Just as we have for other probability distributions, we'll explore the normal distribution's properties, as well as learn how to calculate normal probabilities.
The normal distribution is a subclass of the elliptical distributions. The normal distribution is symmetric about its mean, and is non-zero over the entire real line.
Instructions: This Normal Probability grapher draw a graph of the normal distribution. Please type the population mean \mu μ and population standard deviation \sigma σ, and provide details about the event you want to graph (for the standard normal distribution , the mean is \mu = 0 μ = 0 and the standard deviation is \sigma = 1 σ = 1): There are key features of the normal distribution that make it easy to visually distinguish from other graphs: the peak, asymptotic nature, and symmetry of the graph. The normal curve is essentially a frequency polygon which is tallest (peaks) at the center and gets progressively shorter as you move further into the tails.
Normal distribution. by Marco Taboga, PhD. The normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that plays a central role in probability theory and statistics.TWO NEW 12 INCH TALL GALTON BOARDS WITH PASCAL'S TRIANGLE ARE AVAILABLE! They are probability demonstrators that illustrate randomness, the normal distribution, the binomial distribution, the central limit theorem, regression to the mean and single outcomes with one larger golden bead.
For a perfectly normal distribution, the mean, median, and mode will be the same value, visually represented by the peak of the curve. The normal distribution is often called the bell curve because the graph of its probability density looks like a bell. In a normal distribution, data is symmetrically distributed with no skew. When plotted on a graph, the data follows a bell shape, with most values clustering around a central region and tapering off as they go further away from the center. Normal distributions are also called Gaussian distributions or bell curves because of their shape. Why we love it: This resource walks through multi-step examples and illustrates how the normal distribution can help us estimate the probability of an event.
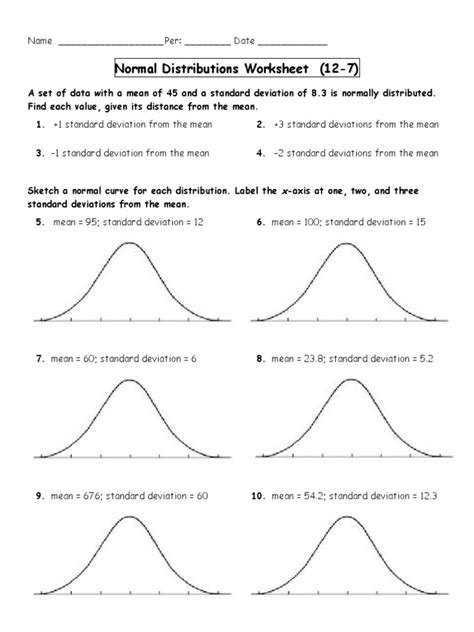
normal distributions worksheet
normal distributions in math
EDCO's board and batten steel siding combines timeless craftsman style with unmatched durability. This innovative metal siding resists chipping, cracking, and peeling, offering virtually maintenance-free beauty in a range of colors.
box that illustrates the normal distribution|normal distributions in math